TADF OLED Emission Zone and Stability Analysis with Water Exposure to Different Layers during Deposition
Reliable devices are essential for the commercialization of OLED technology. OLED materials are notorious for their sensitivity to various substances such as water. For thermally activated delayed emission (TADF) OLED devices, which layers are most water-sensitive is unknown. Work towards understanding how water affects OLED performance is shown.
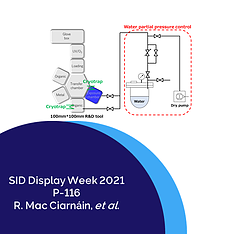
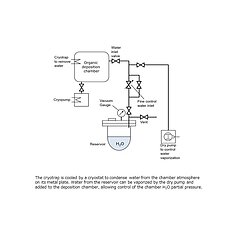
For this purpose, we control the H2O partial pressure of deposition chamber. Individual layers of devices (D0 – D7) are deposited under under H2O partial pressure of 10-6 or 10-7 Pa.
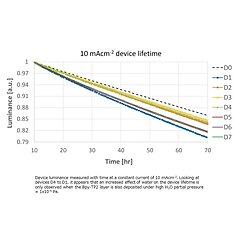
Surprisingly, it is shown that the water effect on the emission layer is negligible compared to other layers in this stack. The lifetime of device D3 is not worse than D4, and D5 is not worse than D6. Therefore, adding water to the emitter layer does not affect the device lifetime. It could be the case that phosphorescent emitters are more susceptible to deactivation by water than TADF emitters, which would be very important for the competitiveness of the technology. The novel chamber design and emission zone measurement outlined in this work could be used to further investigate and understand the effect of water exposure in TADF OLEDs.
SID Digest of Technical Papers 52, 1477-1481 (2021)